From a spark of curiosity and a few slides, now echoed in conference halls, journals, and a double-digit surge of publications worldwide.
Cover Pages
Highligths
Gastroenterology
Quantifying fibrosis in inflammatory bowel diseases – contribution of digital pathology. Jerala et al.Digestive and Liver Diseases, 2025 (8) doi.org/10.1016/j.dld.2025.08.002 (PDF here)
Hepato-oncology
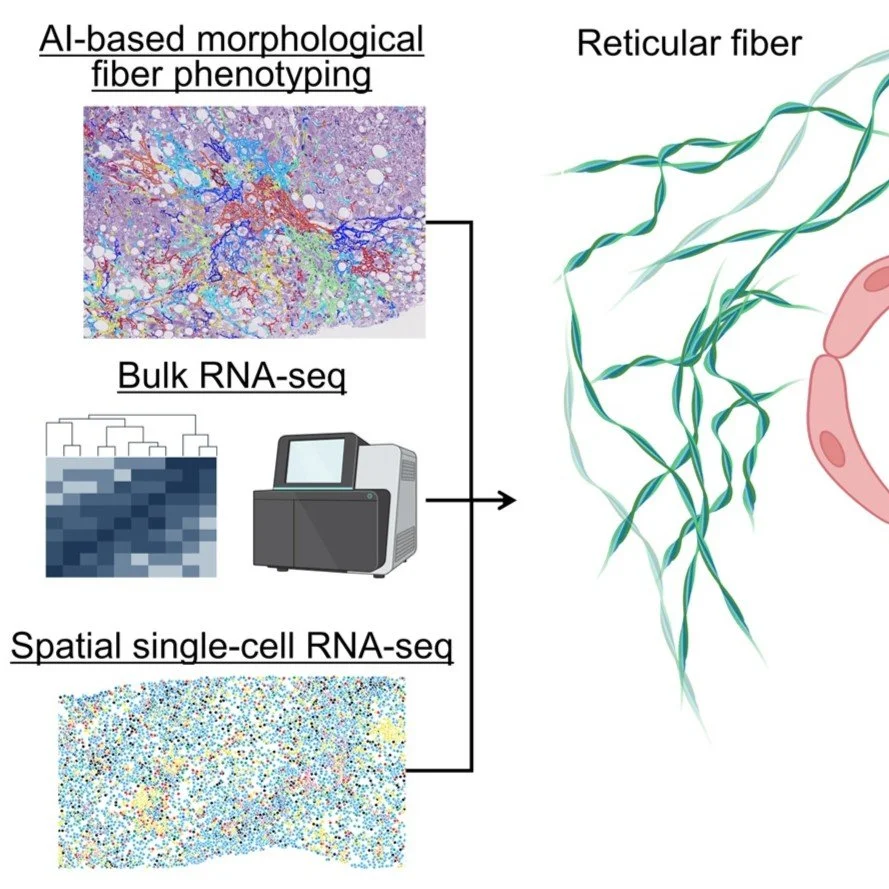
AI-based phenotyping of hepatic fiber morphology to inform molecular alterations in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Fujiwara et al. Hepatology. April 22, 2025. Doi.org/10.1097/HEP.0000000000001360
Hepatology - MASH
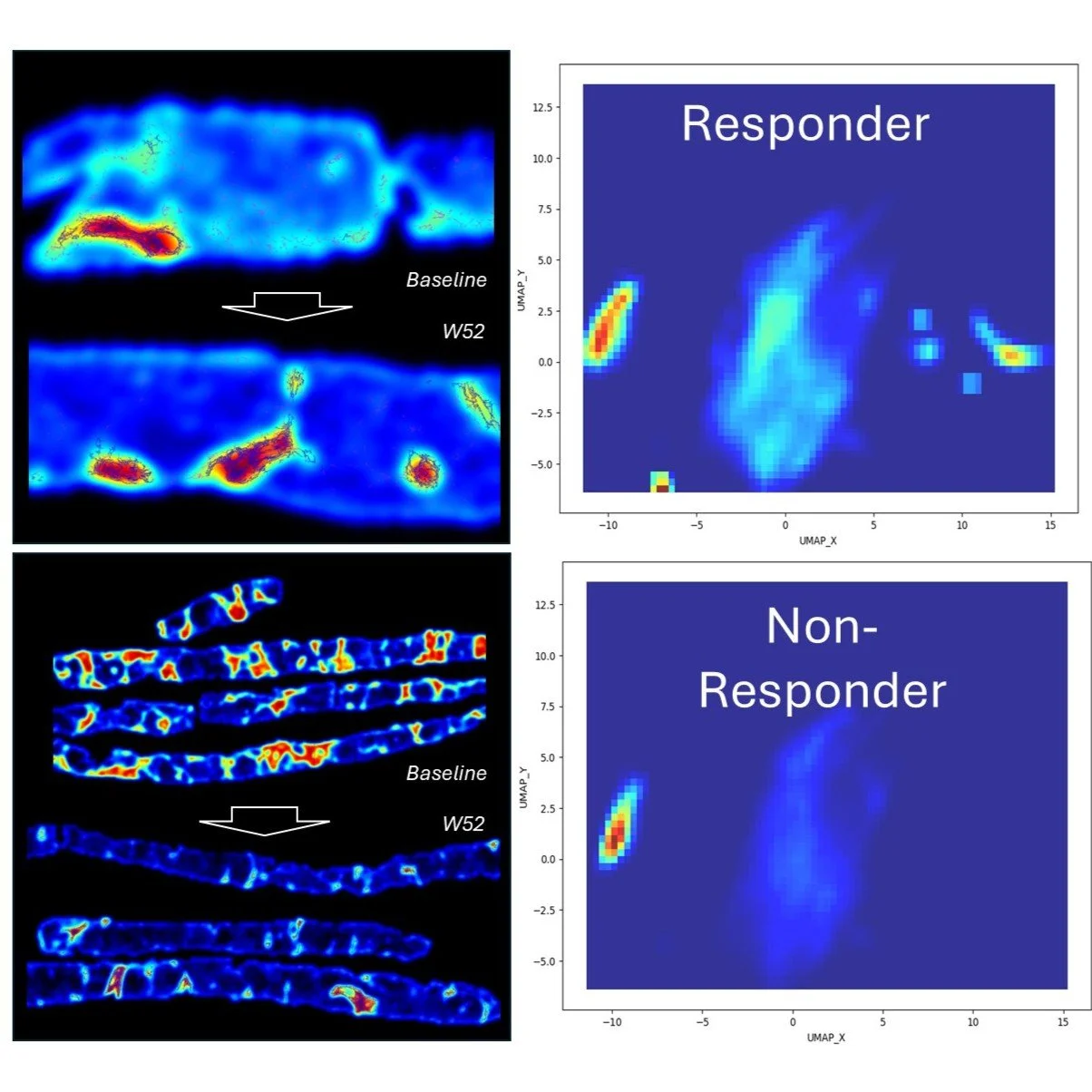
Spatial Computational Histology Stratified Denifanstat Fibrosis Responders in the Phase 2b FASCINATE-2 MASH Study. In collaboration with Sagimet Biosciences. Ratziu et al. AASLD 2025 - Hep. August 2025, (82), S1 (S787) - 10.1097/HEP.0000000000001493
Publications
Hepatology
AI-assisted, single-fiber digital pathology quantification of changes in liver fibrosis after bariatric surgery. Ratziu, Vlad; Petitjean, Louis; Pais, Raluca; Aron-Wisnevsky, Judith; Charlotte, Fréderic; Bedossa, Pierre; Thabut, Dominique; Kara, Leila; Clément, Karine; Petitjean, Mathieu.
Hepatology Communications 10(3):e00900, March 2026. DOI: 10.1097/HC9.0000000000000900
Scar-associated endothelial-stellate cellular crosstalk drives fibrosis resolution in MASH. Kenneth Li, Vardhman Kumar, Tran To, Álvaro González-Domínguez, Janvi Huria, Maylene Yu, Bruno Cogliati, Chittampalli Yashaswini, Mark Miller, Andrea Branch, Bruno Giotti, Alexander Tsankov, Li Chen, Mathieu Petitjean, Jesse Kirkpatrick, Sangeeta Bhatia, Scott Friedman, Shuang Wang
Cell Reports, Volume 45, Issue 2 February 24, 2026 Doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2025.116915
Anti-FAP CAR T cells produced in vivo reduce fibrosis and restore liver homeostasis in metabolic dysfunction–associated steatohepatitis. Chittampalli N. Yashaswini, Bruno Cogliati, Tianyue Qin, Tran To, Thomas Williamson, Tyler E. Papp, Kenneth Li, Raisa Rasul, Li Chen, Adi Lightstone, Haig Aghajanian, Hamideh Parhiz, Joel G. Rurik, Jonathan A. Epstein, and Scott L. Friedman.
Science Translational Medicine, Vol. 18, No. 833 (2026) (Paper here)
Digital Histopathology and AI: A New Era of Liver Fibrosis Quantification. Terraciano et al. Liver International, June 2025, 45(7). https://doi.org/10.1111/liv.70194
Digital Pathology Quantification of the Continuum of Cirrhosis Severity in Human Liver Biopsies. L. Petitjean et al. Liver International (45) 7:e70166, June 16 2025, doi.org/10.1111/liv.70166 with cover page: doi/10.1111/liv.70298
AI-based phenotyping of hepatic fiber morphology to inform molecular alterations in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Fujiwara et al. Hepatology. April 22, 2025. Doi.org/10.1097/HEP.0000000000001360
Mannose reduces fructose metabolism and reverses MASH in human liver slices and murine models in vivo. Hong et al. Hepatology Communications 9(4):e0671, April 2025. Doi.org/ 10.1097/HC9.0000000000000671
Characterizing alcohol-related and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease cirrhosis via fibrotic pattern analysis. Fukushima et al. Scientific Reports volume 14 (Oct 10 2024) Article number: 23679 (2024) doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-73739-4
Characterizing alcohol-related and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease cirrhosis via fibrotic pattern analysis. Fukushima et al. Scientific Reports volume 14 (Oct 10 2024) Article number: 23679 (2024) (doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-73739-4)
Liver fibrosis analysis using digital pathology. Miyaaki et al. Med Mol Morphol. 2024 Sep;57(3):161-166. doi: 10.1007/s00795-024-00395-y
Transposon-based oncogene integration in Abcb4(Mdr2)-/- mice recapitulates high susceptibility to cholangiocarcinoma in primary sclerosing cholangitis. Huang et al. Journal of Hepatology, July 29, 2024 (doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2024.07.016 (PDF))
Aramchol improves hepatic fibrosis in metabolic dysfunction–associated steatohepatitis: Results of multimodality assessment using both conventional and digital pathology. Ratziu etal. Hepatology, Volume 79, issue 4, April 7 2024, DOI: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000980 (PDF)
Digital pathology with artificial intelligence analysis provides insight to the efficacy of anti-fibrotic compounds in human 3D MASH model. Kostadinova et al. Nature, Scientific Reports, Sci Rep 14, 5885 (2024). doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-55438-2
Liver fibrosis phenotyping and severity scoring by quantitative image analysis of biopsy slides. Adam Watson, Louis L. Petitjean, Liver International, November 27 2023, DOI: 10.1111/liv.15768
Digital pathology and artificial intelligence in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: current status and future directions. Ratziu et al. Journal of Hepatology, October 2023. doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2023.10.015
Semaglutide Has Beneficial Effects on Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis in Ldlr-/-.Leiden Mice. Inia et al. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24 (10): 8494. | doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108494
An autocrine signaling circuit in hepatic stellate cells underlies advanced fibrosis in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Wang et al. Science Translational Medicine, 4 Jan 2023, Vol 15, issue 677 | DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.add3949
Breakthroughs in therapies for NASH and remaining challenges, Ratziu et al, Journal of Hepatology 2022 vol. 76 j 1263–1278
Long-term obeticholic acid treatment is associated with improvements in collagen morphometry in patients with primary biliary cholangitis. Kremer et al. Clinical Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2019.09.050
INT-767 improves histopathological features in a diet-induced ob/ob mouse model of biopsy-confirmed non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Roth et al. World J Gastroenterol 2018 January 14; 24(2): 195-210 - doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i2.195 - Weblink here
Long-term obeticholic acid treatment is associated with improvements in collagen morphometry in patients with primary biliary cholangitis. Kremer et al. Clinical Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatolohy | oi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2019.09.050 - here
Gastroenterology
Intratumoral Fibrotic Features are Associated with Lymph Node Metastasis and Recurrence in Patients with Advanced Colon Cancer. Mine et al. Modern Pathology - Volume 38, Issue 11, November 2025, 100828 - doi.org/10.1016/j.modpat.2025.100828
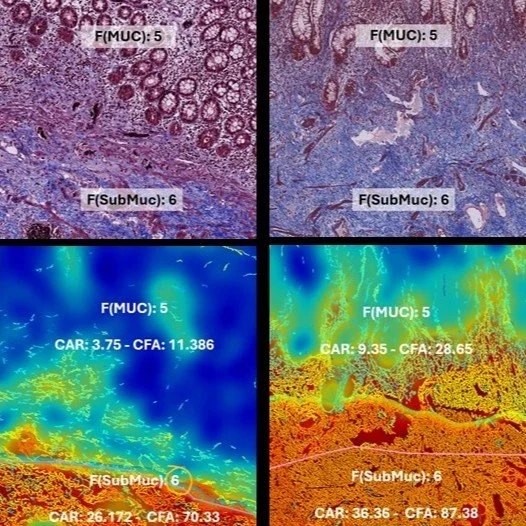
Quantifying fibrosis in inflammatory bowel diseases – contribution of digital pathology. Jerala et al.Digestive and Liver Diseases, 2025 (8) doi.org/10.1016/j.dld.2025.08.002
Thrombospondin 2, matrix Gla protein and digital analysis identified distinct fibroblast populations in fibrostenosing Crohn’s disease. Jerala et al. Scientific Reports volume 14, Article number: 13810 (2024). DOI: doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-64672-7 (PDF)
-
Oncology
Cancer-associated Fibroblast–specific Expression of the Matricellular Protein CCN1 Coordinates Neovascularization and Stroma Deposition in Melanoma Metastasis. Hutchenreuther et al. Cancer Research Communications (2024) 4 (2): 556–570. DOI: 10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-23-0571
Automated fibrosis phenotyping of liver tissue from non-tumor lesions of patients with and without hepatocellular carcinoma after liver transplantation for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Nakamura Y et al. Hepatol Int. 2022;16(3):555-561. doi:10.1007/s12072-022-10340-9 (weblink)
-
Cardiovascular
Collagen Fiber Maturity and Architecture in MVP-Associated Fibrosis Quantified by AI-Powered Pathology. Phookan et al, Cells 2025, 14(19), 1536; https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14191536
Elafibranor improves diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis associated with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in Golden Syrian hamsters. Briand et al. Metabolism. 2021 Jan 11;117:154707. | doi.org 10.1016/j.metabol.2021.154707
-
Aging
Regulation of Female Reproductive Aging by the Spag17 Gene. Ericsson et Al, bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Mar 3:2025.03.01.640648 - doi: 10.1101/2025.03.01.640648
-
Continuous Medical Education
AI-Assisted Pathology Poised to Transform Liver Disease Care
in Medscape Medical News, Marilynn Larkin, September 24, 2024 (weblink)
EASL Congress Six Weeks Later: Mathieu Petitjean’s key Takeaways.
in Surfing the MASH Tsunami: S4-E24.1 - Hosted by Roger Green. August 7, 2024 (weblink)
Conference Abstracts
Hepatology
Digital phenotyping captures regression of liver fibrosis in alcoholic cirrhosis in parallel with abstinence-induced clinical improvement. Horhat et al. AASLD 2025 - Hep. August 2025, (82), S1 (S621) 10.1097/HEP.0000000000001493
Alcoholic hepatitis is associated with distinct phenotypic changes of the hepatic fibrotic matrix as evidenced by quantitative digital pathology: implications for diagnosis and prognosis. Rudler et al. AASLD 2025 - Hep. August 2025, (82), S1 (S623) - 10.1097/HEP.0000000000001493
Spatial Computational Histology Stratified Denifanstat Fibrosis Responders in the Phase 2b FASCINATE-2 MASH Study. In collaboration with Sagimet Biosciences. Ratziu et al. AASLD 2025 - Hep. August 2025, (82), S1 (S787) - 10.1097/HEP.0000000000001493
High-Resolution Collagen Profiling Reveals Stage-Specific Fibrosis Patterns in Pediatric MASLD Using Digital Pathology and UMAP - L. Chen et al. AASLD 2025 - Hep. August 2025, (82), S1 (S739) - 10.1097/HEP.0000000000001493
Digital Pathology identifies intra-stage responders in the ALPINE4 Cirrhosis Study. Rinella et Al. AASLD 2025 - Hep. August 2025, (82), S1 (S822) - collaboration with MGN Pharma- 10.1097/HEP.0000000000001493
Continuous Digital Pathology Scoring Reveals Fibrosis Reversal and Treatment Benefit of Lanifibranor: Insights from a Preclinical Rodent Model. In collaboration with Inventiva Pharma. Wettstein et al. AASLD 2025 - Hep. August 2025, (82), S1 (S1538) -10.1097/HEP.0000000000001493
Combining Digital Pathology and Biomarkers Offer a Translational Framework to Quantify Fibrosis and Lanifibranor Treatment Response in a TAA-Induced Cirrhosis Model. In collaboration with Inventiva Pharma. Chokkakula et al. AASLD 2025 - Hep. August 2025, (82), S1 (S1542) -10.1097/HEP.0000000000001493
High-Resolution Digital Pathology Demonstrates Antifibrotic and Anti-inflammatory Effects of Lanifibranor in Therapeutic Interventions Using TAA-induced Cirrhotic Rodent Models. In collaboration with Inventiva Pharma. Wettstein et al. AASLD 2025 - Hep. August 2025, (82), S1 (S1543) -10.1097/HEP.0000000000001493
Quantitative digital pathology and AI to characterize histological phenotypes of regression in a robust mouse model of human MASH. in collaboration with Pr. Shuang Wang at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, USA. EASL 2025 - Journal of Hepatology 2025 vol. 82(S1) | S600 - Here
Development and validation of a novel fibrosis digital pathology biomarker to predict portal pressure in patients with MASH cirrhosis. in collaboration with Galectin Therapeutics- EASL 2025 - Journal of Hepatology 2025 vol. 82(S1) | S254 - Here
Endothelial-Stellate Cell Crosstalk Underlies Fibrosis Resolution in the Liver. Kenneth Li et al., Hepatology. 80(S1):S1025, October 2024
Sampling variability of liver fibrosis assessed by digital pathology in pre-cirrhotic patients with MASH. in collaboration with Pr. Vlad Ratziu. EASL 2025 - Journal of Hepatology 2025 vol. 82(S1) | S563 - Here
Digital pathology biomarkers describe fibrosis severity and disease activity in the FAT-MASH murine model and response to preventative treatment with mannose. in collaboration with Prs. Jaime Chu and Scott Friedman at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, USA. EASL 2025 - Journal of Hepatology 2025 vol. 82(S1) | S108 - Here
Oral mannose supplementation dampens liver fibrosis in murine MASH model by reducing activated hepatic stellate cell population Hong et al. Hepatology. 80(S1):S1863, October 2024 Poster here
Digital Pathology and AI single-nuclei liver issue panels reveal the quantitative parenchymal involvement of inflammation and steatosis in rodent models of MASH treated with Mannose. Aist et al. AASLD2024. Hepatology. 80(S1):S937, October 2024 Poster Here
Insigths to the Efficacy of clinical anti-fibrotic compounds using digital pathology with AI analysis in a 3D multicellular primary human MASH model. R. Kostadinova et al. Hepatology. 80(S1):S382, October 2024
AI-assisted, quantitative digital pathology-based continuous fibrosis scores perform better than conventional pathology in documenting fibrosis reduction. Ratziu et al. Journal of Hepatology, (2024), S533, 80 (doi.org/10.1016/S0168-8278(24)01597-6) (PDF here)
Single-fiber, high resolution, continuous fibrosis scoring is markedly superior to histology-based conventional staging in identifying fibrosis regression post-bariatric surgery. Ratziu et Al., 2024 EASL conference abstract (poster here)
Evaluation of performance of a cellular profiling technique for quantification of inflammation and steatosis in liver biopsies of patients with MASH. Lightstone et al. Journal of Hepatology, (2024), S591 ( doi.org/10.1016/S0168-8278(24)01736-7 EASL 2024, PDF here)
Novel digital pathology adequacy score benchmarks the performance of pre-analytical method for digital pathology and AI end-to-end tissue assays. L. Petitjean et al. Journal of Hepatology, (2024), S474, 80 (doi.org/10.1016/S0168-8278(24)01458-2 - PDF here)
Evaluation of the performance of AI digital pathology method (FibroNest) on subsections of biopsies to assess performance variability due to region selection. Lightstone et al. Journal of Hepatology, (2024), S597, 80 (doi.org/10.1016/S0168-8278(24)01750-1 - PDF here)
Evaluation of performance of AI digital pathology on the reproducibility and repeatability of fibrosis phenotyping in MASH liver biopsies. Li Chen etal. Journal of Hepatology, (2024), S597, 80 (doi.org/10.1016/S0168-8278(24)01750-1) PDF here
Digital pathology with artificial intelligence analysis provides insight to the efficacy of antifibrotic compounds in human 3D MASH model. Kostadinova et al. International Liver Conference - EASL 2024, Poster here
Novel artificial intelligence-assisted digital pathology quantitative image analysis predicts the occurrence of liver-related clinical events in the multicentric, European, Hepatic OuTcomes and SURvival Fatty Liver Registry (HOTSURFR) study. In collaboration with Pr. Vlad Ratziu and the European HOTSURF Investigators Team. Journal of Hepatology, (2023), S651-S652, 78 (doi.org/10.1016/S0168-8278(23)02001-9) (PDF here)
Novel Digital Pathology quantitative image analysis and AI method detects traits of fibrosis treatment response. In collaboration with Bristol-Myers Squibb and Pr. Arun Sanyal at Virginia Commonwealth University. AASLD 2023, November 10-14 2023, AASLD 2023 Poster of Excellence here, Hep. 78(S1) S1-S2154 2412-C
Digital Pathology quantitative image analysis and AI method detects the treatment effect of pegbelfermin in Cirrhosis patients with a performance that benchmarks manual histological assessment. In collaboration with Bristol-Myers Squibb and Pr. Arun Sanyal at Virginia Commonwealth University. AASLD 2023, November 10-14 2023, Poster here.
Evaluation of the performance of a novel single-nuclei Digital Pathology method for the continuous quantification of Steatosis and Inflammation in liver biopsies and its correlation with NASH-CRN scores in patients with NASH. In collaboration with Pr. Arun Sanyal, Pr. Cynthia Behling an esteemed team of pathologists from the Universities of California. Journal of Hepatology, (2023), S715-S716, 78 ( doi.org/10.1016/S0168-8278(23)02102-5 Poster here)
Artificial Intelligence based digital pathology reveals fatty acid synthase (FASN) inhibitor alone or in combination with semaglutide improves fibrosis in diet-induced obese NASH mice. In collaboration with SAGIMET Biosciences and Gubra ApS. AASLD 2023, November 10-14 2023, Poster Here
Novel artificial intelligence-assisted digital pathology quantitative image analysis predicts the occurrence of liver-related clinical events in the multicentric, European, Hepatic OuTcomes and SURvival Fatty Liver Registry (HOTSURFR) study. In collaboration with Pr. Vlad Ratziu and the European HOTSURF Investigators Team. AASLD 2023 Poster here
Digital Pathology Quantification of Cirrhosis Severity Continuum in Human HCV Liver Biopsies and its Correspondence with Laennec and Beijing stages. In collaboration with Pr. Maria Isabel Fiel and Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, USA Poster here
Evaluation of histological differences between cirrhosis due to alcoholic related liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis using automated fibrosis phenotyping of liver histology. In collaboration with Prs Masanori Fukushima and Hisamitsu Miyaaki and team at Nagasaki University Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences, Nagasaki, Japan Journal of Hepatology, (2023), S178-S179, 78 ( doi.org/10.1016/S0168-8278(23)00705-5) PDF here
Is the hepatic fibrosis histological phenotype in pre- and post-menopausal F2/F3 women the same? In collaboration with Pr. Manuel Romero Gomez and the SeLIVER Group, Seville, Spain Journal of Hepatology, (2023), S335-S336, 78 (doi.org/10.1016/S0168-8278(23)00958-3) see PDF here
Evaluation of anti-fibrotic compounds effect in 3D human NASH model using quantitative digital pathology. In collaboration with Dr. Radina Kostadinova, and InSphero AG Journal of Hepatology, (2023), S327, 78 ( oi.org/10.1016/S0168-8278(23)00942-X) PDF here
Semaglutide has beneficial effects on non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in Ldlr-/-.Leiden mice In collaboration with José A. Inia at the Netherlands Organization for Applied Scientific Research. Journal of Hepatology, (2023), S805, 78 (doi.org/10.1016/S0168-8278(23)02260-2) PDF here
Semaglutide Has Beneficial Effects on Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis in Ldlr-/-.Leiden Mice. José A. Inia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24 (10):8494. | doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108494
Artificial intelligence based digital pathology reveals fatty acid synthase (FASN) inhibitor alone or in combination with semaglutide improves fibrosis in diet-induced obese mice with biopsy confirmed NASH and fibrosis. Wen-Wei Tsai et al. In collaboration with Sagimet BioSciences Poster here
Digital Pathology Image Analysis Accurately Quantifies the Anti-Fibrotic and Anti-Steatotic effects of Mannose in a Well-validated Murine NASH Model. Li Chenet al. keystone Fibrosis 2023 - Poster Here
Histologic assessments by Pathologists and Digital Pathology describe the antifibrotic effect of LPCN 1144. Li Chen, Benjamin J. Bruno, Nachiappan Chidambaram, Cynthia Behling, Mathieu M. Petitjean, Arun J. Sanyal - AASLD 2022 Link to poster here
Quantitative Digital Pathology and Imaging methods demonstrate the consistent reduction of liver fat burden in patient treated with LPCN 1144. Li Chen, Benjamin J. Bruno, Nachiappan Chidambaram, Cynthia Behling, Mathieu M. Petitjean, Arun J. Sanyal - AASLD 2022 - Link to poster here
Digital Pathology Quantification of Intra(“geographic”)-Liver Variation in Human HCV Cirrhosis Liver Biopsies. Louis Petitjean, Xiaofei Zhang, Maria Isabel Fiel, Thomas Shiano, A. J. Sanyal, Mathieu Petitjean - AASLD 2022 - Link to poster here
Novel Digital Pathology quantitative image analysis and AI method detects the treatment effect of NASH drug candidates with a performance that benchmarks Imaging based measurements. Li Chen , Elizabeth Brown, Anne Minnich, Vipul Baxi, Dimple Pandya, Edgar D. Charles, Zachary Goodman, Shuyan Du , Mathieu Petitjean, Arun J. Sanyal, In collaboration with Bristol Myers Squibb. EASL 2022 - See Poster here
Evaluation of the performance of a novel Digital Pathology method for the continuous quantification of Steatosis, Ballooning and Inflammation in liver biopsies and its correlation with NASH-CRN scores in patients with NASH. Louis Petitjean, Li Chen, Aras N. Mattis, Mojgan Hosseini, Michael Goedken, Cynthia Behling, Arun J. Sanyal, Mathieu Petitjean- Journal of Hepatology, (2022), S439, 77 (doi.org/10.1016/S0168-8278(22)01214-4 PDF here)
Etiology-independent fibrosis severity scoring by quantitative digital pathology image analysis. Adam Watson EASL2022 Young Scientist Scholarship Award, Louis Petitjean, Michael Pavlides, Mathieu Petitjean - EASL 2020 - See poster here
Advanced quantitative phenotypic fibrosis and steatosis scoring is markedly superior to histology-based conventional staging in NASH animal models. Li Chen, Dipankar Bhattacharya, Scott Friedman, Mathieu Petitjean. Journal of Hepatology, (2022), S688, 77 (doi.org/10.1016/S0168-8278(22)01694-4 See here)
Quantitative digital Pathology of 3D human NASH models establish continuous scores to evaluate the antifibrotic effects of Selonsertib, Firsocostat and Resmetiron. Louis Petitjean - EASL2022 Young Scientist Full Scholarship Award, Simon Strӧbel, Li C. Chen, Eva Thoma, Radina Kostadinova. Journal of Hepatology, (2022), S481-S482, 77 (International Liver Congress 2022) See poster here
Translational Fibrosis Phenotypes between the 3D Human NASH Spheroidal Model and Clinical NASH Samples. Louis Petitjean, Simon Strӧbel, Li C. Chen, Fancisco Verduguer, Radina Kostadinova, Arun J. Sanyal - See poster here
Is the histological phenotype of Fibrosis different between LEAN and OBESE NASH patients? Michihiro Iwaki, Li Chen, Mathieu Petitjean, Atsushi Nakajima, Vincent Wai-Sun Wong. - Presented at AASLD 2021, #1704 (Poster here)
Evaluation of the multivendor performance of a novel histology-based fibrosis phenotypic composite score and its correlation with NASH-CRN Fibrosis scores in patients with NASH Li Chen, Michael Lung, Cynthia Behling, Anthony Azzara, Diane Shevell, Arun J. Sanyal, Mathieu Petitjean . Journal of Hepatology, (2020), S421, 73 (doi.org/10.1016/S0168-8278(20)31326-X AASLD 2020 Poster Here)
3D human NASH model as a screening-based discovery approach for selecting and prioritizing drug candidates. Simon Ströbel, Jana Rupp, Katia Fiaschetti, Agnieszka Pajak, Katarzyna Sanchez, Mathieu Petitjean, Li Chen, Manuela Bieri, Armin Wolf, Sue Grepper, Francisco Verdeguer, Radina Kostadinova. Journal of Hepatology, (2022), S488, 77 (doi.org/10.1016/S0168-8278(22)01307-1)
LPCN 1144 Therapy demonstrates Histologic Benefits in the Phase2 LiFT Study in NonAlcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) Subjects. Arun J Sanyal, Benjamin J Bruno, Kilyoung Kim, Shadi Mehraba, Kongnara Papangkorn, Anthony DelConte, Nachiappan Chidambaram and Mahesh V Patel. Presented at AASLD 2021 (Late Breaker abstract LP41)
Combination of an Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase Inhibitor and Fibroblast Growth Factor-19 Reduced Tissue Triglyceride Content and Fibrosis in a 3D Human Liver Microtissue Model of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Wen-Wei Tsai, Manuela Bieri, Sue Grepper, Eva Thoma, James L. Trevaskis.. Presented at AASLD 2021, #1621 (Poster Here)
FG19 Gene therapy reduces Steatosis but not Inflammation and Fibrosis in Two Mouse Models of NASH – Martin Borch Jensen, Chris Carrico, Linda Chio, Ian Driver, Daniel Fuentes, Akela Kuwahara, Francisco LePort, Chris Towne. Gordian Biotechnology. AASLD 2021 Poster Here.
Therapeutic Candidates in a single Animal Model of NASH Martin Borch Jensen, Chris Carrico, Linda Chio, Ian Driver, Daniel Fuentes, Akela Kuwahara, Francisco LePort, Chris Towne- Gordian Biotechnology, San Francisco, CA – ASLD 2021 Poster Here
Digital Pathology Image Analysis Accurately Quantifies Anti-fibrotic and Anti-steatotic effects of FXR Agonists Using Multiple Histological Methods. Li Chen (1), Mary Erickson (2), Luciano Adorini (2), Jonathan Roth (2), Mathieu Petitjean (1)- 1 PharmaNest, Princeton, NJ, USA, 2 Intercept Pharmaceuticals, San Diego, CA, USA Presented at AASLD 2021, #1908 (Poster Here)
Continuous staging of NASH Patients at low (F1) Fibrosis Severity: Evaluation of the performance of a novel histology-based fibrosis phenotypic composite score and predictive AI tools. Li Chen Dmitry Fedorov, Mathieu Petitjean, Benjamin J. Bruno, Kilyoung Kim, Cynthia Behling, Anthony DelConte, Nachiappan Chidambaram. Presented at AASLD 2021, #1587 (Poster Here)
In-Vitro human 3D NASH model as a screening-based discovery approach for selecting and prioritizing drug candidates. Simon Strӧbel, Jana Rupp, Katia Fiaschetti, Agnieska Pajat, Katarzyna Sanchez, Mathieu M. Petitjean, Li Chen, Manuela Bieri, Armin Wolf, Sue Grepper Eva Thoma, Radina Kostadinova. Presented at AASLD 2021, #1906 (Poster Here)
Evaluation of anti-fibrotic effects of compounds in human 3D NASH model using phenotypic quantification of fibrosis digital pathology images. Simon Strӧbel, Mathieu M. Petitjean, Eva Thoma, Radina Kostadinova. Presented at AASLD 2021, #1362 (Poster Here)
A rapid 3D in Vitro Screening-based discovery approach for selecting and prioritizing NASH drug Candidates. Simon Ströbel , Radina Kostadinova,Jana Rupp, Katia Fiaschetti, Agnieszka Pajak, Katarzyna Sanchez, Mathieu Petitjean, Li Chen, Manuela Bieri, Armin Wolf, Eva Thoma. Presented at AASLD 2021 Poster # PO-2210
Novel Phenomics NASH In Vitro Assay. Radina Kostadinova, Mathieu Petitjean, Presented by InSphero AG and PharmaNest Inc at 2021 Society of Toxicology Meeting.
Novel phenotypic image analysis of 3D NASH model generate quantitative and continuous scores for the evaluation of fibrosis in vitro. Mathieu M. Petitjean, Radina Kostadinova, Li Chen, Simon Strӧbel, Eva Thomas. AASLD 2020 (Poster here)
Evaluation of a novel histology-based fibrosis phenotypic composite score and its correlation with NASH-CRN Fibrosis scores in patients with NASH. Li Chen, Michael Lung, Cynthia Behling, Arun Sanyal, Mathieu Petitjean. EASL2020 (Poster here)
Microscopy‐based fibrosis phenotypic analysis of rodent and adult NASH cohorts reveal translational traits of fibrosis progression and severity. Li Chen, Anthony Azzara, Mathieu Petitjean, Arun Sanyal. Journal of Hepatology, (2020), S519-S520, 73 (doi.org/10.1016/S0168-8278(20)31516-6 (see here)
Fibrosis phenotypic analysis of collagen stained liver histology sections discern anti-fibrotic agents in DDC- induced cholangitis mouse model. Li Chen, Richard Chen, Liangsu Wang, Mathieu Petitjean. Journal of Hepatology, (2020), S520, 73 (doi.org/10.1016/S0168-8278(20)31517-8 EASL2020 see here)
Evaluation of a novel two‐photon microscopy‐based fibrosis phenotypic composite score and its correlation with serum neo-epitope collagen biomarkers in patients with NASH. Li Chen, Yi Luo, Faridoddin Mirshahi, Anthony Azzara, Arun Sanyal, Mathieu Petitjean. In collaboration with Bristol-Myers Squibb Company. Poster presentation at AASLD 2019. Poster Here
Development of an Optimal Continuous Pediatric Fibrosis Score to Assess Severity and Progression of Fibrosis in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). Elena Reynoso, Li Chen, Mathieu Petitjean, Cynthia Behling, Joel Lavine. Poster presentation at AASLD 2019. Poster Here
Automated Steatosis Morphometric Scores Benchmark the Pathology-Based Quantification of Steatosis in Pediatric NASH/NAFLD Populations. Zachary Pitkowsky, Li Chen, Elena Reynoso, Mathieu Petitjean, Cynthia Behling, Joel Lavine Journal of Hepatology, (2022), S446, 77 (doi.org/10.1016/S0168-8278(22)01227-2, see Here)
Automated Morphometric Fibrosis Phenotyping of NAFLD Biopsies Digital Images Helps Classify NASH-Type 1 Vs NASH-Type 2 in Early Fibrosis Pediatric Patients. Mathieu Petitjean, Li Chen, Elena Reynoso, Cynthia Behling, Joel E. Lavine. Poster presentation at AASLD 2019. Poster Here
Quantitative Assessment of Liver Septal Fibrosis Severity Using Morphometric Analysis, Li Chen PhD ., Anthony Azzara PhD, Mathieu Petitjean PhD. In collaboration with Bristol Myers Squibb -Presented at NASH-TAG 2018 Poster here
Gastroenterology
Single Fiber Digital Pathology and AI quantifies fibrosis severity from superficial layers of surgical resections of patients with Crohn’s disease. Chen et al, Digestive Diseases Week 2024 , May 18-21, 2024 Poster here
Contribution of Digital Pathology and AI to the quantification of fibrosis in Crohn’s disease. Li Chen et al. Poster here
-
Respiratory
Bleomycin Induced IPF in the DIO mouse: a new translational model to evaluate drugs targeting IPF. F. Briant et Al. Keystone Symposium: Fibrosis: Inflammation, Drivers, and Therapeutic Resolution - December 8-12, 2024. Poster here.
Comparison of histological phenotype by FibroNest of human IPF and pre-clinical rodent models of lung fibrosis. Francesca Ruscitti et Al, and in collaboration with Chiesi Pharma. 22 International Colloquium on Lung and Airway Fibrosis, October 12-16 2024, (Poster PDF here)
Quantitative Digital Pathology and AI method characterizes the histologic phenotypes of fibrosis severity in bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis mouse model. Chen et al, American Thoracic Society 2024 - May 18-22, 2024 Poster here
Comparison of the Histological Phenotypes of Lung Fibrosis induced by Oropharyngeal and Subcutaneous Bleomycin Administration in Mouse. Louis Petitjean et al. in collaboration with TNO- Keystone Fibrosis 2023 - Poster Here
Describing the Progression of Bleomycin-Induced Fibrosis in a Mouse-Lung Model via Oropharyngeal Administration. Christa de Ruiter et al. in collaboration with TNO, Netherlands Organisation for Applied Scientific Research - Keystone Fibrosis and Inflammation 2022 (Poster Here)
Novel morphometric image analysis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis models generates quantitative and continuous scores for the evaluation of fibrosis. Florence Marsais, Li Chen, Mathieu Petitjean, Philippe Pujuguet. In collaboration with Galapagos SA,presented at 2020 Keystone Fibrosis and Tissue Repair, March 19-22 2020 - Poster Here
-
Nephrology
Quantitative image analysis reveals podocytes effacement and kidney fibrosis in SDT fatty rats with impaired renal function by unilateral nephrectomy and salt supplement diet. Briand et Al, ISN-World Congress of Nephrology, April 13-16 2024 Poster here
Quantitative Image Analysis Reveals the Benefits of Dapagliflozin on Glomerulosclerosis, Podocytes Effacement and Kidney Fibrosis in the SDT Fatty Rat Model of Diabetic Nephropathy. Briand et al. CKD Summit 2024, Poster here
Novel morphometric image analysis of Chronic Kidney Disease STNx model generates quantitative and continuous scores for the evaluation of fibrosis. Teodelina Mirabella, Matthew Rankin, Li Chen, Mathieu Petitjean, Matthew Bryer, In collaboration with Janssen Pharmaceuticals. Presented at 2020 Keystone Fibrosis and Tissue Repair, March 19-22 2020- Poster Here
-
Cardiovascular
Novel digital pathology quantifies peripapillary fibrosis in mitral valve prolapse. Morningstar et al. 2024 Keystone Fibrosis and Inflammation, Poster Here
Artificial intelligence-assisted digital pathology characterizes the fibrosis phenotypes in Cardiomyopathy. Lightstone et al. Keystone Fibrosis and Inflammation, March 3-9 2024, Poster Here
-
Autoimune Fibrotic Diseases
Digital Pathology Accurately Quantifies Skin Fibrosis Severity in SPAG17 Gene Knockout Animal Model. John Varga et al. Keystone Fibrosis and Inflammation, March 3-9 2024, Poster Here
Comparison of the Histological Phenotypes of Lung Fibrosis induced by Oropharyngeal and Subcutaneous Bleomycin Administration in Mouse. Louis Petitjean et al. in collaboration with TNO- Keystone Fibrosis 2023 - Poster Here
Evaluation of the performance of a novel Digital Pathology score for the evaluation of Fibrosis in patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. Darise-Farris, Kathy Sivils et al. Oklahoma Medical Research Foundation (OMRF), Oklahoma City, OK | Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc, Horsham, PA.- Keystone Fibrosis 2023 - Poster Here
Single-fiber Digital Pathology Image Analysis accurately quantifies the severity of the fibrosis phenotype in ane xperimental rodent model of systemic sclerosis. Silvia Speca, David Launay et al. Keystone 2023- Poster Here
Advanced Skin Image Analysis for Evaluation of Bleomycin- induced Skin Fibrosis in Mouse Scleroderma Model. Li Chen, Louis Petitjean, Christa de Ruiter, Joline Attema, Reinout Stoop. In collaboration with TNO, Netherlands Organisation for Applied Scientific Research- Presented at Keystone Fibrosis and Inflammation 2022 (Poster Here)
-
Muscular Degeneration - Duchenne
Digital Pathology Image Analysis Accurately detects the Anti-Fibrotic effects of Gene Therapy in Mouse Models of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Lightstone et Al. Keystone Fibrosis and Inflammation, March 3-9 2024, Poster Here
-
Oncology
Digital Pathology Quantification Reveals Fibrotic Signatures Linked to Early Recurrence in patients with Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma. L. Chen et al. AASLD 2025 - Hep. August 2025, (82), S1 (S1576) -10.1097/HEP.0000000000001493
Histological phenotypes of regression in advanced liver fibrosis using quantitative digital pathology in a rodent model of cirrhotic human NASH with HCC. in collaboration with Pr. Scott Friedman at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, NY.EASL 2025 - Journal of Hepatology 2025 vol. 82(S1) | S601 - Here
Functional role of CD44+ cancer stem cells in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Dr. Paula Cantallops Vila at Institut d’I nvestigacions biomèdiques August Pi i Sunyer (IDIBAPS), Barcelona, Spain
Cancer-associated fibroblast-specific expression of the matricellular protein CCN1 coordinates neovascularization and stroma deposition in melanoma metastasis. Hutchenreuther et al., Keystone Fibrosis and Inflammation, March 3-9 2024, March 2024: Poster Here
Transposon-based Oncogenes Integration in AbcB4(Mdre2)-/- mice recapitulates high susceptibility to Cholangiocarcinoma in Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis. In collaboration with Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA and Pr Yury Popov. EASL 2023, JUNE 21-24, 2023
SB CCA.Mdr2-/-, a new mouse model of Cholangiocarcinoma arising in the PSC-like settings of progressive biliary injury and fibrosis. Pinzhu Huang, Guangyan Wei , Shuangshuang Zhao, Disha Badlani, Kahini Vaid, Li Chen, Mathieu Petitjean, Xin Chen, Gregory Gores, Yury Popov- AASLD 2021 (Poster #1183)
New mouse model of cholangiocarcinoma arising in the setting of progressive biliary injury and fibrosis. Pinzhu Huang, Guangyan Wei, Shuangshuang Zhao, Disha Badlani, Kahini Vaid, Li Chen, Mathieu Petitjean, Xin Chen, Gregory Gores , Yury Popov.Presented at AASLD 2021 Poster # PO-677 Here
Automated Fibrosis Phenotyping of NASH non-tumorous lesions Digital Images Helps Classify HCC and non-HCC NASH patients who underwent liver transplantation. Hisamitsu Miyaaki, Yuko Akazawa, Li Chen, Mathieu Petitjean. Presented at AASLD 2020 (Poster here)
ASK1 Inhibition Reduces Progression of Liver Cirrhosis and Prevents Tumor Development in the BALS/c.Mdr2-/- Mouse Model of Biliary Fibrosis. G. Wei, P. An, K, Vaid, G. Budas, A. Mikels-Vigdal, M. Kuand, Y. Popov- In collaboration with Gilead Sciences, San Presented at AASDL 2018. Poster here.
-
Systemic - Cross Organ
Does subcutaneous fibrosis predict the severity of liver fibrosis? Onoiu et al. AASLD 2025 - Hep. August 2025, (82), S1 (S768) - 10.1097/HEP.0000000000001493
Contributions of Digital Pathology and Artificial Intelligence to the quantification of histological fibrosis in several organs and biological systems. M. Petitjean and Li Chen, Keystone Symposium: Fibrosis: Inflammation, Drivers, and Therapeutic Resolution - December 8-12, 2024. Poster here.